Vue、Vue.extend、Vue.component、vm.mixins、vm.extends的区别及选项合并策略
Vue、Vue.extend、Vue.component、vm.mixins、vm.extends的区别
Vue
Vue构造器(类)主要用来创建vue根实例,参数是一个选项对象;vue中组件是一个带有名字的可复用vue实例(组件也是一个个的vue实例),其本质也是借助Vue构造器(类)来生成的,所以组件定义的参数和Vue构造器需要的参数基本一致,仅有的例外是像el这样根实例特有的选项。1
2
3
4new Vue({
el:'#app',
render:h=>h(App)
})
Vue.extend
- 基于
Vue类,创建一个子类,参数是一个包含组件选项的对象 - 主要用于vue中创建可复用的组件,见
Vue.component - 一些特殊场景
- 例如在指令中使用Vue.extend创建一个vue实例,并用$mount挂载到dom中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11import BaseLoadingSpinner from 'Base/BaseLoadingSpinner'
const ExtendLoading = Vue.extend({
components: {
BaseLoadingSpinner
},
template: '<div style="text-align:center;font-size:20px;"><BaseLoadingSpinner/></div>'
})
const MyLoading = new ExtendLoading().$mount()
document.body.appendChild(MyLoading.$el)
- 例如在指令中使用Vue.extend创建一个vue实例,并用$mount挂载到dom中
Vue.component
- 注册\查询全局组件
- 内部借助
Vue.extend来实现1
2
3
4
5Vue.component('global-component', Vue.extend(baseOptions));
//传入一个选项对象(自动调用 Vue.extend),等价于上行代码.
Vue.component('global-component', baseOptions);
// 获取注册的组件(始终返回构造器)
var MyComponent = Vue.component('my-component')
vm.mixins
Vue实例(组件)上的方法,主要利用混入来扩展组件的功能,它接收一个混入对象的数组- 混入对象是一个
Vue选项对象,Vue构造器能使用的选项,混入对象都可以使用 - 如果混入对象和组件原有选项出现同名选项如何处理?
- 生命周期hook及watch
- 同名的生命周期hook,将按照minxins传入顺序依次调用
- 不同名的生命周期hook,将按照原先的生命周期顺序调用
- 同名的watch和生命周期hook的处理方式相同,也是按照minxins传入顺序依次调用
- 同名的生命周期hook,将按照minxins传入顺序依次调用
- 非生命周期hook及watch的选项字段
- 同名的,都以当前组件为主(覆盖混入对象的字段)
- 非同名的,合并
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
const mixin1 = {
data() {
return {
text: 'mixin1',
test: {
source: 'from mixin1'
}
}
},
computed: {
computedText() {
return `I am ${this.text}`
}
},
created() {
console.log('mixin1 text', this.text)
console.log('mixin1 computedText', this.computedText)
console.log('mixin1 test', this.test)
}
}
const mixin2 = {
data() {
return {
text: 'mixin2',
test: {
source: 'from mixin2'
}
}
},
computed: {
computedText() {
return `I am ${this.text}`
}
},
created() {
console.log('mixin2 text', this.text)
console.log('mixin2 computedText', this.computedText)
console.log('mixin2 test', this.test)
},
mounted() {
console.log('mixin2 mounted')
}
}
const compa = {
name: 'CompA',
// mixins: [mixin1],
mixins: [mixin1, mixin2],
// extends: mixin2,
data() {
return {
text: 'compa',
test: {
source: 'from compa',
own: 'compa'
}
}
},
computed: {
computedText() {
return `I am ${this.text}`
}
},
created() {
console.log('compa text', this.text)
console.log('compa computedText', this.computedText)
console.log('compa test', this.test)
},
render: h => h('div', 'compa')
}
const App = {
name: 'App',
render: h => h(compa)
}
const baseOptions = {
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
}
new Vue(baseOptions)
- 生命周期hook及watch
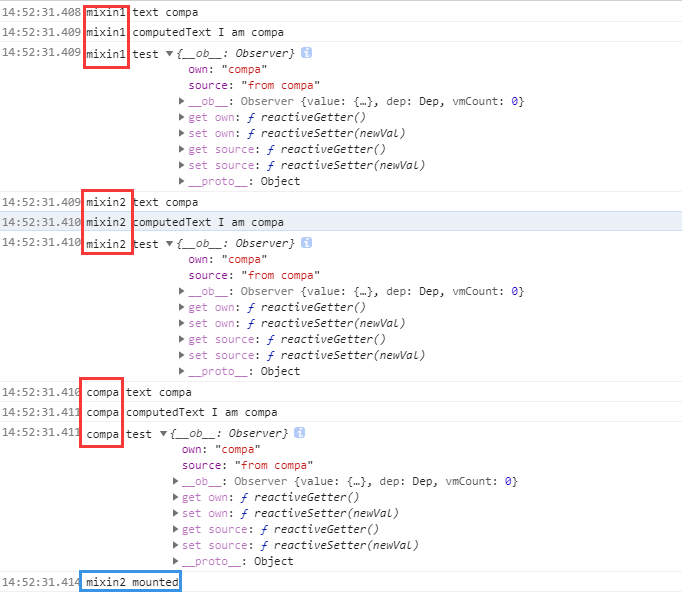
- 可以看到,同名的created钩子,按照传入顺序依次调用,compa的mounted钩子在所有的created执行完后再执行的;同名的非hook、watch的选项,如data、computed都优先使用当前组件的,所以最终own、source都是compa中定义
vm.extends
- 作用基本和mixins类似,都用来扩充组件功能,但有细微却别
- 区别
mixins是将一个个独立的功能扩充到当前组件上,相当于为当前组件添加某种能力,先有功能,再将功能添加到当前组件上;利用的是组合思想vm.extends是继承一个组件,并在其之上再添加功能,相当于扩充一个已有组件的功能;利用的是继承思想- mixins接收一个数组,extends接收一个组件
- 既然是继承,肯定会出现同名冲突的情况,其处理策略和
vm.mixins选项合并策略一样;其实Vue.extend、vm.mixins、vm.extends他们的选项合并策略都是一样的;
选项合并策略
- vue中选项合并的策略,主要用在
Vue.extend、vm.mixins、vm.extends等需要合并选项对象的地方 - vue版本
2.5.21
前置知识
默认合并策略
1 | // src\core\util\options.js |
parentVal对应父选项,childVal对应子选项,只有在子选项没传时才使用parentVal,否则都使用childVal- 针对不同的选项字段,vue有不同的合并策略
父、子选项对象如何界定
使用
vm.mixins时- 混入对象为父选项对象、当前组件(vm)选项为子选项对象
1
2
3Vue.component('A',{ // A视为子选项对象
mixins:[B] // B视为父选项对象
})
- 混入对象为父选项对象、当前组件(vm)选项为子选项对象
使用
vm.extends时- 继承的组件选项为父选项对象,当前组件(vm)选项为子选项对象
1
2
3Vue.component('A',{ // A视为子选项对象
extends:B // B视为父选项对象
})
- 继承的组件选项为父选项对象,当前组件(vm)选项为子选项对象
使用
Vue.extend时Vue.extend接收的选项对象为子选项对象,Vue默认选项对象为父选项对象1
Vue.extend(B) // B视为子选项对象,Vue默认选项对象为父选项对象
递归合并对象
1 | // src\core\util\options.js |
混入属性到目标对象中
1 | // src\shared\util.js |
el、propsData合并策略
- 使用默认合并策略(child选项没传时才使用parent选项,否则都用child选项)
- 子选项对象优先
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17// src\core\util\options.js
/**
* Options with restrictions
*/
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
strats.el = strats.propsData = function (parent, child, vm, key) {
if (!vm) {
warn(
`option "${key}" can only be used during instance ` +
'creation with the `new` keyword.'
)
}
// 使用默认合并策略(child没传时才使用parent,否则都用child)
return defaultStrat(parent, child)
}
}
data合并策略
- 由于data在组件中是一个函数,所以会先调用,然后通过
mergeData将父选项对象递归合并到子选项对象中1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49// src\core\util\options.js
/**
* Data
*/
export function mergeDataOrFn (
parentVal: any,
childVal: any,
vm?: Component
): ?Function {
if (!vm) {
// in a Vue.extend merge, both should be functions
if (!childVal) {
return parentVal
}
if (!parentVal) {
return childVal
}
// when parentVal & childVal are both present,
// we need to return a function that returns the
// merged result of both functions... no need to
// check if parentVal is a function here because
// it has to be a function to pass previous merges.
return function mergedDataFn () {
// 递归合并选项对象(将parentVal递归合并到childVal中)
return mergeData(
typeof childVal === 'function' ? childVal.call(this, this) : childVal,
typeof parentVal === 'function' ? parentVal.call(this, this) : parentVal
)
}
} else {
return function mergedInstanceDataFn () {
// instance merge
const instanceData = typeof childVal === 'function'
? childVal.call(vm, vm)
: childVal
const defaultData = typeof parentVal === 'function'
? parentVal.call(vm, vm)
: parentVal
if (instanceData) {
// 递归合并选项对象(将defaultData递归合并到instanceData中)
return mergeData(instanceData, defaultData)
} else {
return defaultData
}
}
}
}
components、directives、filters合并策略
- 这三个被vue视为
ASSET - 使用原型委托将
最终选项对象的__proto__指向了父选项对象,并调用extend函数将子选项对象的所有属性混入到最终选项对象,最终效果就是,子选项对象中找不到时,会顺着原型链找到父选项对象,结果是子选项对象的字段会优先被使用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30// src\shared\constants.js
export const ASSET_TYPES = [
'component',
'directive',
'filter'
]
// src\core\util\options.js
/**
* Assets
*
* When a vm is present (instance creation), we need to do
* a three-way merge between constructor options, instance
* options and parent options.
*/
function mergeAssets (
parentVal: ?Object,
childVal: ?Object,
vm?: Component,
key: string
): Object {
const res = Object.create(parentVal || null) // res.__proto__指向parentVal
if (childVal) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && assertObjectType(key, childVal, vm)
return extend(res, childVal) // 将子选项对象所有属性混入到res
} else {
return res
}
}
props、methods、inject、computed合并策略
- 先调用
extend将父选项对象所有属性混入到空对象obj上,再调用extend将子选项对象所有属性混入到obj上;最终还是子选项对象的字段会被优先使用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26/**
* Other object hashes.
*/
strats.props =
strats.methods =
strats.inject =
strats.computed = function (
parentVal: ?Object,
childVal: ?Object,
vm?: Component,
key: string
): ?Object {
if (childVal && process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assertObjectType(key, childVal, vm)
}
if (!parentVal) return childVal
const ret = Object.create(null) // 空对象
extend(ret, parentVal) // 先混入parentVal所有属性
if (childVal) extend(ret, childVal) // 再混入childVal所有属性,当childVal和parentVal出现同名属性时,将覆盖parentVal
return ret
}
provide合并策略
- 其和data合并策略是一样的
- 它使用data合并策略中的
mergeDataOrFn方法来合并1
strats.provide = mergeDataOrFn
生命周期hook
- 同名的生命周期hook,会合并到一个数组中,并且父选项对象的hook会先执行;
- 不同名的生命周期hook,会按照生命周期,依次调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21// src\core\util\options.js
/**
* Hooks and props are merged as arrays.
*/
function mergeHook (
parentVal: ?Array<Function>,
childVal: ?Function | ?Array<Function>
): ?Array<Function> {
return childVal
? parentVal
? parentVal.concat(childVal) // 父子选项对象都存在,则直接合并到一个数组中
: Array.isArray(childVal)
? childVal
: [childVal]
: parentVal
}
LIFECYCLE_HOOKS.forEach(hook => {
strats[hook] = mergeHook
})
watch合并策略
- 其合并策略和生命周期hook类似;父子选项对象的watch会合并到同一个数组中,并且父选项的watch在前
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40// src\core\util\options.js
/**
* Watchers.
*
* Watchers hashes should not overwrite one
* another, so we merge them as arrays.
*/
strats.watch = function (
parentVal: ?Object,
childVal: ?Object,
vm?: Component,
key: string
): ?Object {
// work around Firefox's Object.prototype.watch...
if (parentVal === nativeWatch) parentVal = undefined
if (childVal === nativeWatch) childVal = undefined
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (!childVal) return Object.create(parentVal || null)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assertObjectType(key, childVal, vm)
}
if (!parentVal) return childVal
const ret = {}
extend(ret, parentVal) // 混入父选项对象所有属性
for (const key in childVal) {
let parent = ret[key]
const child = childVal[key]
if (parent && !Array.isArray(parent)) {
parent = [parent]
}
ret[key] = parent
? parent.concat(child) // 合并到一个数组中
: Array.isArray(child)
? child : [child]
}
return ret
}
当同时使用Vue.extend、vm.extends、vm.mixins时选项如何合并
1 |
|
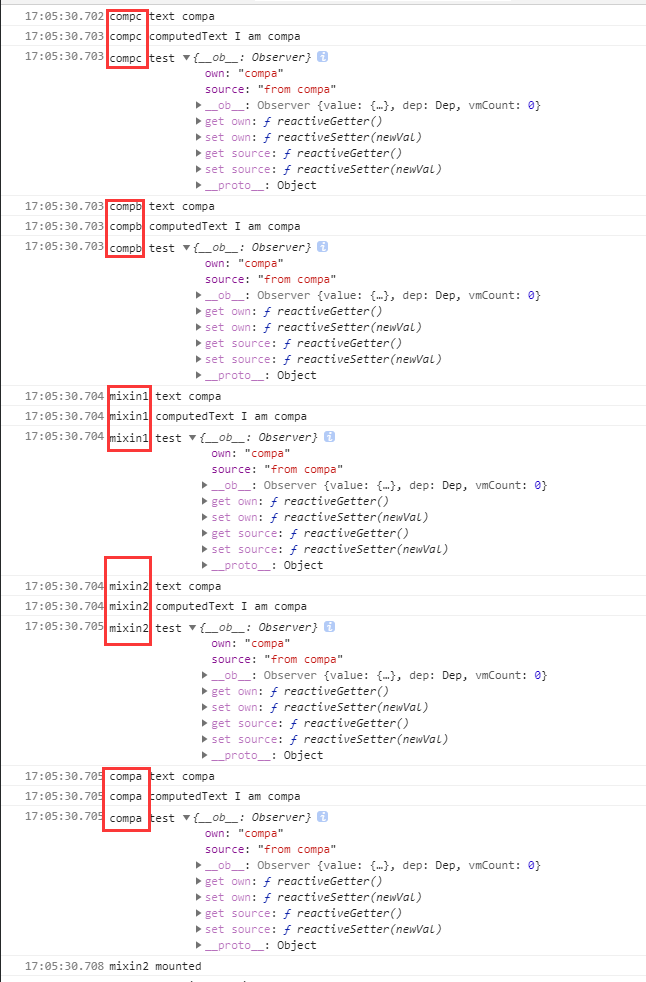
- 会看到
created钩子被调用的顺序依次为compc、compb、mixin1、mixin2、compa - data都为
compa - 总结
- extend、extends、mixins同时使用时
hook及watch的执行顺序:extend>extends>mixins>当前组件非hook及watch会使用当前组件的值
- extend、extends、mixins同时使用时
总结
Vue.extend、vm.extends、vm.mixins使用相同的选项合并策略- 未出现同名选项时,会使用类似
Object.assign的机制来合并选项const newOption=Object.assign({},parentVal,childVal)
- 出现同名选项时
hook、watch选项出现同名时,会将其合并到一个数组中,并且父选项对象的先执行非hook、watch选项出现同名时,优先使用子选项对象的值
- 未出现同名选项时,会使用类似
- 同时使用
Vue.extend、vm.extends、vm.mixins时- 未出现同名选项时,会使用类似
Object.assign的机制来合并选项 - 出现同名选项时
hook及watch的执行顺序:extend>extends>mixins>当前组件非hook及watch会使用当前组件的值
- 未出现同名选项时,会使用类似
参考
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010095089
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000007087912